Partials
Partials allow areas of the page to be updated with new content by the server without causing the browser to reload the page. They make your website feel more app-like because only the parts of the page that need to be updated will be updated.
Enabling partials
Partials are enabled by adding a f-client-nav attribute to an HTML element and
wrapping one or more areas in the page with a
<Partial name="my-partial">-component.
The quickest way to get started is to enable partials for every page in
routes/_app.tsx by making the following changes.
import { PageProps } from "$fresh/server.ts";
+ import { Partial } from "$fresh/runtime.ts";
export default function App({ Component }: PageProps) {
return (
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>My Fresh app</title>
</head>
- <body>
+ <body f-client-nav>
+ <Partial name="body">
<Component />
+ </Partial>
</body>
</html>
);
}By adding the f-client-nav attribute, we enable partials for every element
beneath the <body>-tag. To mark an area of the page as a partial we wrap it
with a <Partial>-component with a unique name.
Behind the scenes, when the user clicks an <a>-tag, Fresh fetches the new page
and only pulls out the relevant content out of the HTML response. When it finds
a matching partial area it will update the content inside the partial.
InfoThenameprop of the<Partial>component is expected to be unique among Partials. That’s how Fresh knows which parts of the response need to go on the current page.
InfoPassing f-client-nav={false} disables client side navigation for all
elements below the current node.
Optimizing partial requests
By default, with f-client-nav set, Fresh fetches the full next page and only
picks out the relevant parts of the response. We can optimize this pattern
further by only rendering the parts we need, instead of always rendering the
full page. This is done by adding the f-partial attribute to a link.
- <a href="/docs/routes">Routes</a>
+ <a href="/docs/routes" f-partial="/partials/docs/routes">Routes</a>When the f-partial attribute is present, Fresh will navigate to the page URL
defined in the href attribute, but fetch the updated UI from the URL specified
in f-partial instead. This can be a highly optimized route that only delivers
the content you care about.
Let’s use a typical documentation page layout as an example. It often features a main content area and a sidebar of links to switch between pages of the documentation (marked green here).
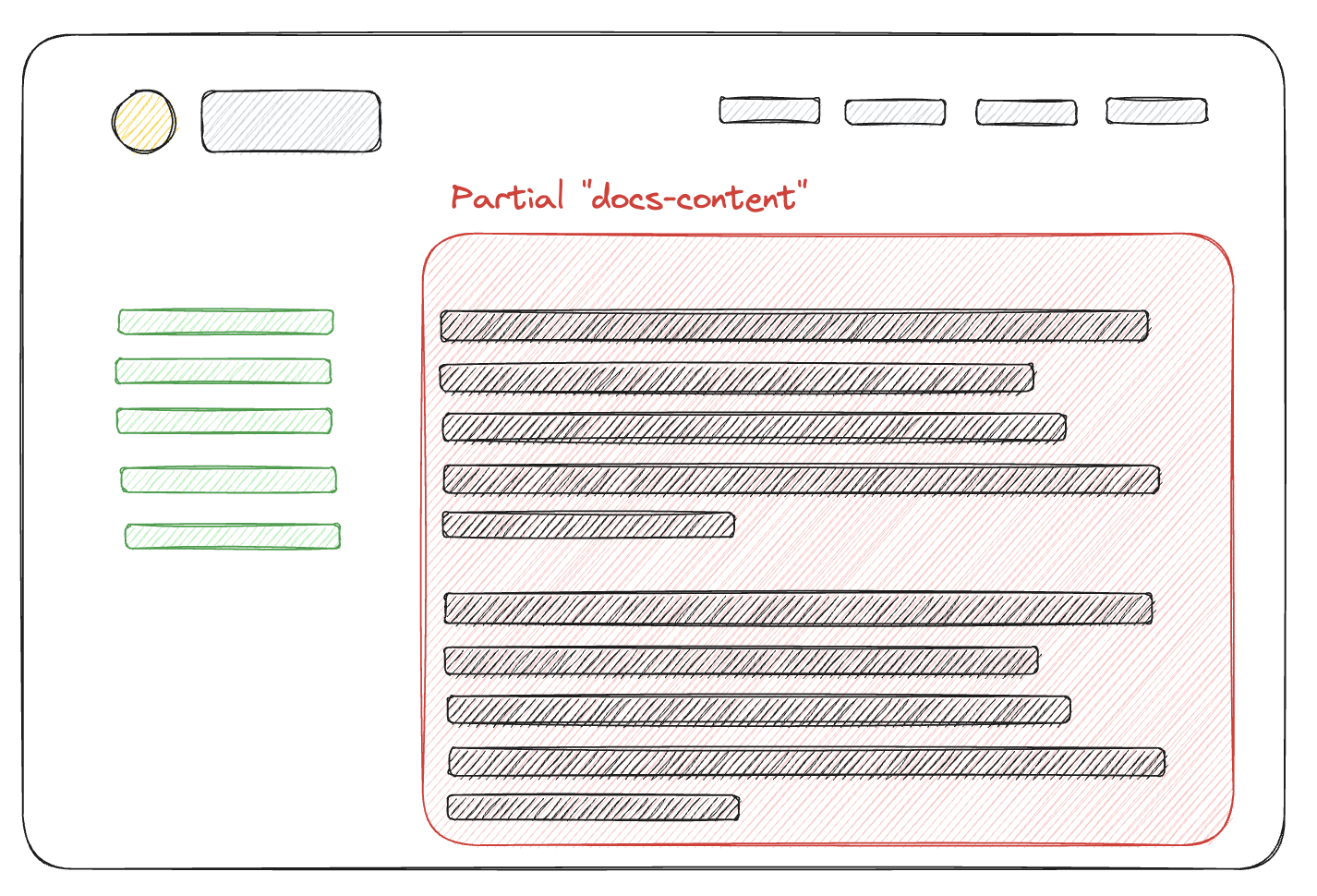
The code for such a page (excluding styling) might look like this:
export default defineRoute(async (req, ctx) => {
const content = await loadContent(ctx.params.id);
return (
<div>
<aside>
<a href="/docs/page1">Page 1</a>
<a href="/docs/page2">Page 2</a>
</aside>
<Partial name="docs-content">
{content}
</Partial>
</div>
);
});An optimal route that only renders the content instead of the outer layout with the sidebar might look like this respectively.
import { defineRoute, RouteConfig } from "$fresh/server.ts";
import { Partial } from "$fresh/runtime.ts";
// We only want to render the content, so disable
// the `_app.tsx` template as well as any potentially
// inherited layouts
export const config: RouteConfig = {
skipAppWrapper: true,
skipInheritedLayouts: true,
};
export default defineRoute(async (req, ctx) => {
const content = await loadContent(ctx.params.id);
// Only render the new content
return (
<Partial name="docs-content">
{content}
</Partial>
);
});By adding the f-partial attribute we tell Fresh to fetch the content from our
newly added /partials/docs/[id].tsx route.
<aside>
- <a href="/docs/page1">Page 1</a>
- <a href="/docs/page2">Page 2</a>
+ <a href="/docs/page1" f-partial="/partials/docs/page1">Page 1</a>
+ <a href="/docs/page2" f-partial="/partials/docs/page2">Page 2</a>
</aside>With this in place, Fresh will navigate to the new page when clicking any of the two links and only load the content rendered by our optimized partial route.
Currently,
f-partialis scoped to<a>,<button>and<form>elements. This might be extended to more elements in the future.
Sending multiple Partials at the same time
A neat aspect of partials in Fresh is that a response can return as many partials as desired. That way you can update multiple unrelated areas on your page in one single HTTP response. A scenario where this is useful are online shops for example.
export default function AddToCartPartial() {
return (
<>
<Partial name="cart-items" mode="append">
{/* Render the new cart item here */}
</Partial>
<Partial name="total-price">
<p>Total: {totalPrice} €</p>
</Partial>
</>
);
}Both partials will be applied to the current page.
Replacement mode
By default the whole content inside a partial will be replaced, but there are
scenarios where you want to prepend or append new content instead. This can be
achieved by adding the mode prop to a Partial component.
replace- Swap out the content of the existing partial (default)prepend- Insert the new content before the existing contentappend- Insert the new content after the existing content
Personally, we’ve found that the append mode is really useful when you have an
UI which displays log messages or similar list-like data.
export default function LogView() {
const lines = getNewLogLines();
return (
<Partial name="logs-list" mode="append">
{lines.map((line) => {
return <li key={line}>{line}</li>;
})}
</Partial>
);
}InfoWhen picking theprependorappendmode, make sure to add keys to the elements.
Bypassing or disabling Partials
If you want to exempt a particular element from triggering a partial request
like on a particular link, form or button, you can opt out of it by setting
f-client-nav={false} on the element or one of the ancestor elements.
<body f-client-nav>
{/* This will cause a partial navigation */}
<a href="/docs/page1">With partials</a>
{/* This WONT cause a partial navigation */}
<a href="/docs/page1" f-client-nav={false}>No partials</a>
{/* This WONT cause a partial navigation on any elements below */}
<div f-client-nav={false}>
<div>
<a href="/docs/page1">No partials</a>
</div>
</div>
</body>;Whenever an element is clicked Fresh checks if it has the f-client-nav
attribute and if it is set to true. If the element itself doesn’t have such an
attribute, it will check if any of the ancestor elements has it. If an element
was found with a truthy f-client-nav attribute a partial request will be
triggered. If there is no such attribute or if it’s set to false, no partial
request will occur.